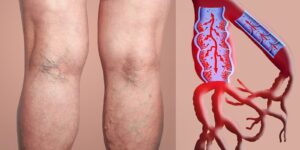
 Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. Seniors are at a higher risk for DVT due to age-related changes in circulation, mobility, and overall health. Understanding this condition, recognizing its symptoms, and addressing the unique challenges in diagnosis and treatment are essential for preventing complications like pulmonary embolism.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs. Seniors are at a higher risk for DVT due to age-related changes in circulation, mobility, and overall health. Understanding this condition, recognizing its symptoms, and addressing the unique challenges in diagnosis and treatment are essential for preventing complications like pulmonary embolism.
DVT in the Elderly
As individuals age, their blood circulation tends to slow, and the risk of clot formation increases. Seniors are also more likely to have conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, or varicose veins, which can contribute to DVT. Long periods of immobility — whether due to a hospital stay, recovery from surgery, or even long travel—can further raise the likelihood of developing a clot.
Certain medications, such as hormone therapy or blood pressure drugs, can also influence clotting factors in the blood. Understanding these risk factors is key to preventing DVT.
Symptoms
DVT often develops silently, but there are some symptoms to watch for:
- Swelling: Typically in one leg, usually around the calf or ankle.
- Pain or Tenderness: A cramping sensation in the leg that may worsen when standing or walking.
- Skin Changes: Redness or discoloration around the affected area, and sometimes warmth to the touch.
- Fatigue in the Leg: A feeling of heaviness or discomfort in one leg.
If you or a loved one experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately, as untreated DVT can lead to life-threatening complications.
Challenges in Diagnosis and Treatment
DVT can be difficult to diagnose because its symptoms may mimic other conditions, such as muscle strain or cellulitis. Ultrasound imaging is often used to confirm the presence of a clot.
Treatment typically involves anticoagulant medications to prevent clot growth and new clot formation. For seniors, managing treatment can be more challenging due to potential interactions with other medications or underlying health conditions. Compression stockings and increased mobility are also crucial parts of the recovery process.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the risk of DVT in seniors, recognizing symptoms, and pursuing prompt treatment are vital for preventing serious complications. Stay vigilant, stay mobile, and always consult your healthcare provider for the best prevention and treatment strategies.
